Smaller countries should band together to sustain multilateral free trade
Martin Wolf

Where does deepening economic conflict between the US and China leave the rest of the world, especially historic allies of the US? In normal circumstances, the latter would stand beside it. The EU, after all, shares many of its concerns about Chinese behaviour. Yet these are not normal circumstances. Under Donald Trump, the US has become a rogue superpower, hostile, among many other things, to the fundamental norms of a trading system based on multilateral agreement and binding rules. Indeed, US allies, too, are a target of the wave of bilateral bullying.
So what are American allies to do as the US and China battle? This is not just about Mr Trump. His focus on bilateral trade balances may even be relatively manageable. Worse, a large proportion of Americans shares a deepening hostility not just to China’s behaviour, but to the fact of a rising China.
We are also seeing a big shift in conservative thinking. In 2005, Robert Zoellick, deputy secretary of state, argued that China should “become a responsible stakeholder” in the international system. Recently, Mike Pompeo, secretary of state, has indicated a different perspective. Foreign affairs specialist Walter Russell Mead describes Mr Pompeo’s animating idea as follows: “Where liberal internationalists believe the goal of American global engagement should be to promote the emergence of a world order in which international institutions increasingly supplant nation-states as the chief actors in global politics, conservative internationalists believe American engagement should be guided by a narrower focus on specific US interests.” In brief, the US no longer sees why it should be a “responsible stakeholder” in the international system. Its concept is, instead, that of 19th century power politics, in which the strong dictate to the weak.
This is relevant to trade, too. It is a canard that the trading system was based on the notion that international institutions should supplant nation states. The system was built on the twin ideas that states should make multilateral agreements with one another and that confidence in such agreements should be reinforced by a binding dispute settlement system. This would bring stability to the conditions of trade, on which international businesses rely.
All this is now at risk. The spread of the tariff war and the decision to limit the access to US technology of Huawei, China’s only world-leading advanced technology manufacturer, seem aimed at keeping China in permanent inferiority. That is certainly how the Chinese view it.
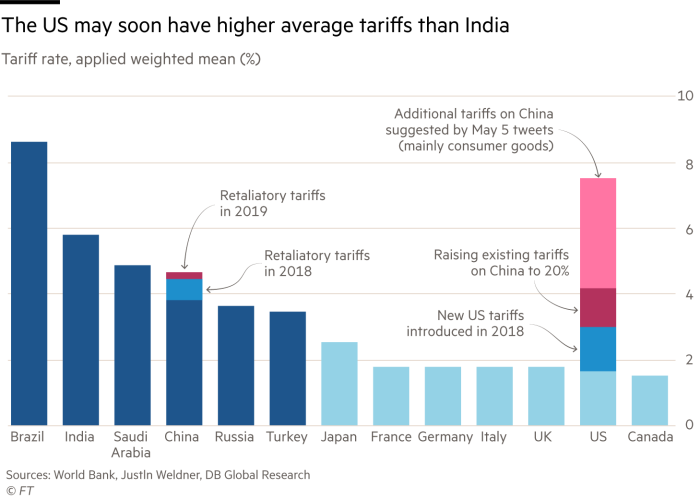
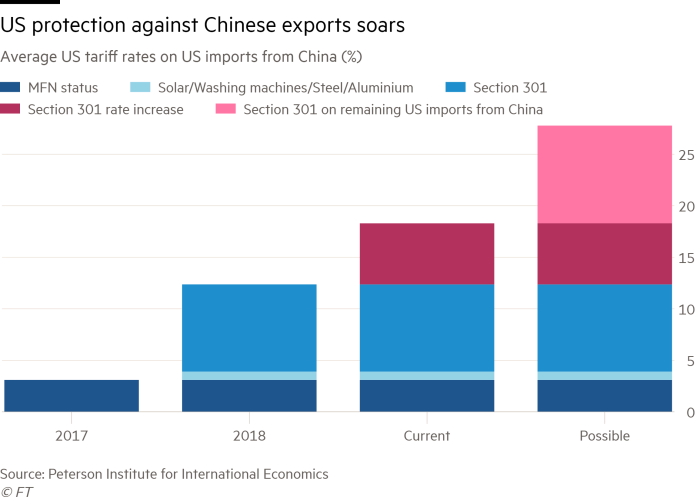
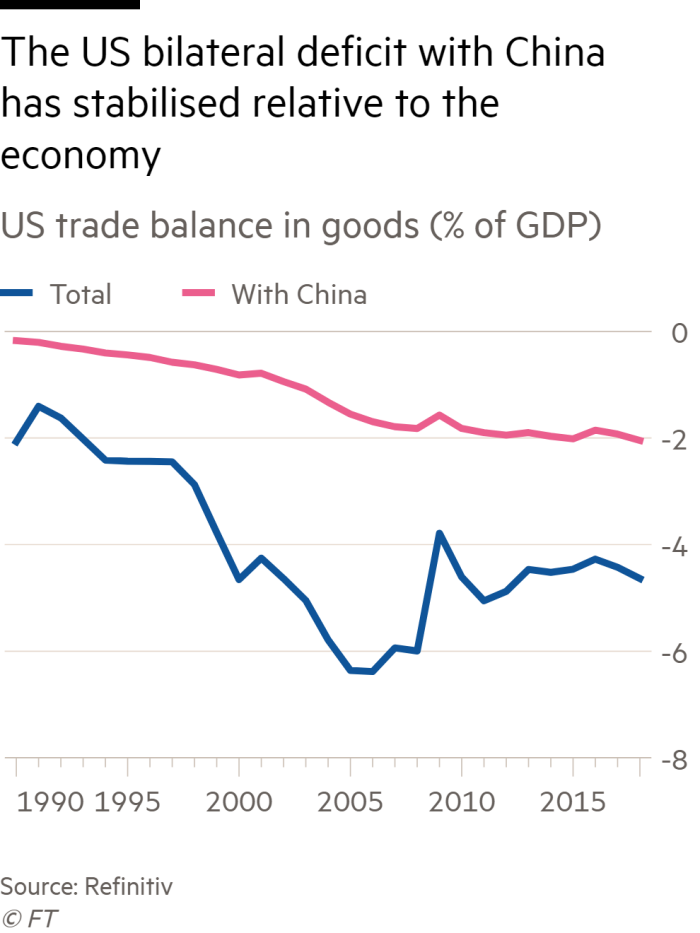
The trade war is also turning the US into a significantly protectionist country, with weighted-average tariffs possibly soon higher than India’s. A paper from the Peterson Institute for International Economics states, that “Trump is . . . threatening tariffs on China that are not far from the average level of duties the United States imposed with the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930.” Tariffs may even stay this high, because the US’s negotiating demands are too humiliating for China to accept. These levies will also lead to diversion to other suppliers. Tariffs may then spread to the latter, too: bilateralism is often a contagious disease. Contrary to Mr Trump’s protestations, the costs are also being borne by Americans, especially consumers and farm exporters. Ironically, many of the worst hit counties are in Republican control. (See charts.)
Some might conclude that the high costs mean that the conflict cannot be sustained, particularly if stock markets are disrupted. An alternative and more plausible outcome is that Mr Trump and China’s Xi Jinping are “strongmen” leaders who cannot be seen to yield. The conflict will then either remain frozen or, more likely, worsen as relations between the two superpowers become increasingly poisoned.
Where does this leave US allies? They should not support American attempts to thwart China’s rise: that would be unconscionable. They should indicate where they agree with US objectives on trade and technology and, if possible, sustain a common position on these issues, notably between the EU and Japan. They should uphold the principles of a multilateral trading system, under the auspices of the World Trade Organization. If the US succeeds in rendering the dispute system inquorate, the other members could agree to abide by an informal mechanism instead.
Most significantly, it should be possible to sustain liberal trade, at the expense of the US and China. Anne Krueger, former first deputy managing director of the IMF, notes in a column that, by its own foolish decision to reject the Trans-Pacific Partnership, the US suffers from WTO legal discrimination against its exports to members of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership, which replaced TPP. The EU also has free trade agreements with Canada and Japan.
This is good. But they can go further. Countries that see the benefits of a strong trading order should turn such FTAs into a “global FTA of the willing”, in which any country willing to accept the commitments could participate. One might even envisage a future in which participants in such a global FTA would defend its members against illegal trade assaults from non-members, via co-ordinated retaliation.
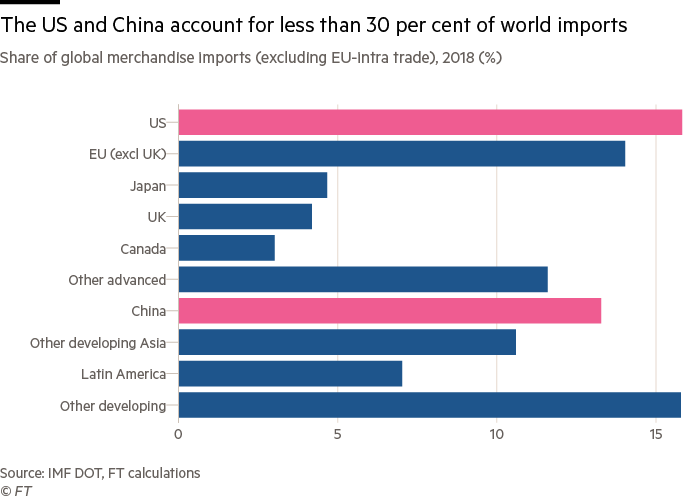
Hostility between the US and China is a threat to global peace and prosperity. Outsiders cannot halt this conflict. But they are not helpless. If the big powers stand outside the multilateral trading system, others can step in. They are, in aggregate, huge players. They should dare to act as such.
0 comments:
Publicar un comentario